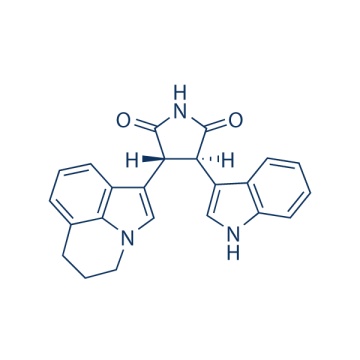
Tivantinib (ARQ 197) 905854-02-6
Product Description
.cp_wz table {border-top: 1px solid #ccc;border-left:1px solid #ccc; } .cp_wz table td{border-right: 1px solid #ccc; border-bottom: 1px solid #ccc; padding: 5px 0px 0px 5px;} .cp_wz table th {border-right: 1px solid #ccc;border-bottom: 1px solid #ccc; padding: 5px 0px 0px 5px;}
Molecular Weight:
369.42 Tivantinib (ARQ 197) is the first non-ATP-competitive c-Met Inhibitor with Ki of 0.355 μM, little activity to Ron, and no inhibition to EGFR, InsR, PDGFRα or FGFR1/4. Phase 3.
Biological Activity
ARQ-197 has been shown to prevent HGF/c-met induced cellular responses
in vitro. ARQ-197 possesses antitumor activity; inhibiting proliferation
of A549, DBTRG and NCI-H441 cells with IC50 of 0.38, 0.45, 0.29 μM.
Treatment with ARQ-197 results in a decrease in phosphorylation of the
MAPK signaling cascade and prevention of invasion and migration. In
addition, ectopic expression of c-Met in NCI-H661, a cell line having no
endogenous expression of c-Met, causes it to acquire an invasive
phenotype that is also suppressed by ARQ-197.
Although the addition of
increasing concentrations of ARQ-197 does not significantly affect the Km of ATP, exposure of c-Met to 0.5 μM ARQ-197 decreased the Vmax of c-Met by approximately 3-fold. The ability of ARQ-197 to decrease the Vmax without affecting the Km of ATP confirmed that ARQ-197 inhibits c-Met
through a non–ATP-competitive mechanism and may therefore account for
its high degree of kinase selectivity. ARQ-197 prevents human
recombinant c-Met with a calculated inhibitory constant Ki of
approximately 355 nM.
Although the highest concentration of ATP used is
200 μM, the potency of ARQ-197 against c-Met is not reduced by using
concentrations of ATP up to 1 mM. ARQ-197 blocks c-Met phosphorylation
and downstream c-Met signaling pathways. ARQ-197 suppresses constitutive
and ligand-mediated c-Met autophosphorylation and, by extension, c-Met
activity, in turn leading to the inhibition of downstream c-Met
effectors. ARQ-197 induction of caspase-dependent Apoptosis is increased
in c-Met–expressing human cancer cells including HT29, MKN-45, and
MDA-MB-231 cells.
All three xenograft models treated with ARQ-197 display reductions in
tumor growth: 66% in the HT29 model, 45% in the MKN-45 model, and 79% in
the MDA-MB-231 model.
In these xenograft studies, no significant body
weight changes following oral administration of ARQ-197 at 200 mg/kg are
observed. Pharmacodynamically, the phosphorylation of c-Met in human
colon xenograft tumors (HT29) is strongly inhibited by ARQ-197, as
assessed by a dramatic reduction of c-Met autophosphorylation 24 hours
after a single oral dose of 200 mg/kg of ARQ-197.
This same dosage in
mice exhibits that tumor xenografts are exposed to sustained plasma
levels of ARQ-197, consistent with the observed pharmacodynamic
inhibition of c-Met phosphorylation and inhibition of proliferation of
c-Met harboring cancer cell lines.
Plasma levels of ARQ-197 10 hours
after dosing are determined to be 1.3 μM, more than 3-fold above the
biochemical inhibitory constant of ARQ-197 for c-Met. Therefore, ARQ-197
is able to suppress its target in vivo in the xenografted human tumor
tissue. In conclusion, ARQ-197 inhibits the growth of c-Met-dependent
xenografted human tumors.
c-Met SDS-PAGE in vitro kinase assay
Recombinant c-Met protein (100 ng) is preincubated with increasing
concentrations of ARQ-197 for 30 minutes at room temperature. Following
preincubation, 100 μM of poly-Glu-Tyr substrate and various
concentrations of ATP containing 5 μCi of [γ-32P]ATP are added to the
reaction mixture.
The reaction is incubated for 5 minutes at room
temperature and then stopped by the addition of 5 μL of
SDS-polyacrylamide gel, reducing sample buffer. The samples are then
loaded onto a 7.5% acrylamide gel and SDS-PAGE is performed. The
phosphorylated poly-Glu-Tyr substrates are ultimately visualized by
autoradiography. c-Met activity is quantified by densitometry.
Method
HT29, MKN-45, and MDA-MB-231 cells are seeded in black 96-well plates at 5 × 103 cells per well overnight in a medium with 10% FBS. The next day, cells
are treated with increasing concentrations of ARQ-197 (0.03-10 μM) for
24, 32, and 48 hours at 37 °C. After ARQ-197 treatment, the
drug-containing medium is removed and cells are incubated for at least
10 minutes in a labeling solution (10 mM HEPES, 140 mM NaCl, and 6 mM
CaCl2) containing 2 μg/mL Hoescht 33342 (blue channel),
500-times diluted Annexin V-FITC (green channel), and 1 μg/mL propidium
iodide (red channel).
High-content image acquisition and analysis are
carried out. The program is set to take four images per well. The
exposure time is set at 16.7 ms/10% gain, 500 ms/35% gain, and 300
ms/30% gain for the 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole, FITC, and rhodamine
channels, respectively. Images are processed and the numbers of positive
cells for each channel and each condition are determined.
In addition,
HT29 cells are treated with increasing concentrations of ARQ-197 for 32
hours in the absence or the presence of 25, 50, and 100 μM ZvAD-FMK
(irreversible general Caspase Inhibitor), and the same procedures are
undertaken. All experiments are done in triplicate. To determine whether
the apoptotic effect is due to c-Met inhibition, the effect of ARQ-197
when glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) and c-Met are
knocked down using siRNA is investigated.
HT29, MKN-45, and MDA-MB-231
cells are transfected with a nontargeted control siRNA, a gapgh-targeted
control siRNA, or a met-targeted siRNA. After 3 days, c-Met, GAPDH, and
β-actin expression levels are determined using specific antibodies. To
determine if the effect is caspase dependent, HT29, MKN-45, and
MDA-MB-231 cells are transfected with a met-targeted siRNA for 2 days
and incubated in the absence or the presence of increasing
concentrations of ZvAD-FMK for 1 additional day. A nontargeted siRNA and
a gapgh-targeted siRNA (siRNA GAPDH) are also transfected in parallel,
as controls. Cells are then stained with Annexin V-FITC and propidium
iodide, and the percentage of apoptotic cells is determined.
Contact us if you need more details on 905854-02-6. We are ready to answer your questions on packaging, logistics, certification or any other aspects about Tivantinib 905854-02-6、ARQ 197 905854-02-6. If these products fail to match your need, please contact us and we would like to provide relevant information.
Molecular Weight:
369.42 Tivantinib (ARQ 197) is the first non-ATP-competitive c-Met Inhibitor with Ki of 0.355 μM, little activity to Ron, and no inhibition to EGFR, InsR, PDGFRα or FGFR1/4. Phase 3.
Biological Activity
ARQ-197 has been shown to prevent HGF/c-met induced cellular responses
in vitro. ARQ-197 possesses antitumor activity; inhibiting proliferation
of A549, DBTRG and NCI-H441 cells with IC50 of 0.38, 0.45, 0.29 μM.
Treatment with ARQ-197 results in a decrease in phosphorylation of the
MAPK signaling cascade and prevention of invasion and migration. In
addition, ectopic expression of c-Met in NCI-H661, a cell line having no
endogenous expression of c-Met, causes it to acquire an invasive
phenotype that is also suppressed by ARQ-197.
Although the addition of
increasing concentrations of ARQ-197 does not significantly affect the Km of ATP, exposure of c-Met to 0.5 μM ARQ-197 decreased the Vmax of c-Met by approximately 3-fold. The ability of ARQ-197 to decrease the Vmax without affecting the Km of ATP confirmed that ARQ-197 inhibits c-Met
through a non–ATP-competitive mechanism and may therefore account for
its high degree of kinase selectivity. ARQ-197 prevents human
recombinant c-Met with a calculated inhibitory constant Ki of
approximately 355 nM.
Although the highest concentration of ATP used is
200 μM, the potency of ARQ-197 against c-Met is not reduced by using
concentrations of ATP up to 1 mM. ARQ-197 blocks c-Met phosphorylation
and downstream c-Met signaling pathways. ARQ-197 suppresses constitutive
and ligand-mediated c-Met autophosphorylation and, by extension, c-Met
activity, in turn leading to the inhibition of downstream c-Met
effectors. ARQ-197 induction of caspase-dependent Apoptosis is increased
in c-Met–expressing human cancer cells including HT29, MKN-45, and
MDA-MB-231 cells.
All three xenograft models treated with ARQ-197 display reductions in
tumor growth: 66% in the HT29 model, 45% in the MKN-45 model, and 79% in
the MDA-MB-231 model.
In these xenograft studies, no significant body
weight changes following oral administration of ARQ-197 at 200 mg/kg are
observed. Pharmacodynamically, the phosphorylation of c-Met in human
colon xenograft tumors (HT29) is strongly inhibited by ARQ-197, as
assessed by a dramatic reduction of c-Met autophosphorylation 24 hours
after a single oral dose of 200 mg/kg of ARQ-197.
This same dosage in
mice exhibits that tumor xenografts are exposed to sustained plasma
levels of ARQ-197, consistent with the observed pharmacodynamic
inhibition of c-Met phosphorylation and inhibition of proliferation of
c-Met harboring cancer cell lines.
Plasma levels of ARQ-197 10 hours
after dosing are determined to be 1.3 μM, more than 3-fold above the
biochemical inhibitory constant of ARQ-197 for c-Met. Therefore, ARQ-197
is able to suppress its target in vivo in the xenografted human tumor
tissue. In conclusion, ARQ-197 inhibits the growth of c-Met-dependent
xenografted human tumors.
c-Met SDS-PAGE in vitro kinase assay
Recombinant c-Met protein (100 ng) is preincubated with increasing
concentrations of ARQ-197 for 30 minutes at room temperature. Following
preincubation, 100 μM of poly-Glu-Tyr substrate and various
concentrations of ATP containing 5 μCi of [γ-32P]ATP are added to the
reaction mixture.
The reaction is incubated for 5 minutes at room
temperature and then stopped by the addition of 5 μL of
SDS-polyacrylamide gel, reducing sample buffer. The samples are then
loaded onto a 7.5% acrylamide gel and SDS-PAGE is performed. The
phosphorylated poly-Glu-Tyr substrates are ultimately visualized by
autoradiography. c-Met activity is quantified by densitometry.
Method
HT29, MKN-45, and MDA-MB-231 cells are seeded in black 96-well plates at 5 × 103 cells per well overnight in a medium with 10% FBS. The next day, cells
are treated with increasing concentrations of ARQ-197 (0.03-10 μM) for
24, 32, and 48 hours at 37 °C. After ARQ-197 treatment, the
drug-containing medium is removed and cells are incubated for at least
10 minutes in a labeling solution (10 mM HEPES, 140 mM NaCl, and 6 mM
CaCl2) containing 2 μg/mL Hoescht 33342 (blue channel),
500-times diluted Annexin V-FITC (green channel), and 1 μg/mL propidium
iodide (red channel).
High-content image acquisition and analysis are
carried out. The program is set to take four images per well. The
exposure time is set at 16.7 ms/10% gain, 500 ms/35% gain, and 300
ms/30% gain for the 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole, FITC, and rhodamine
channels, respectively. Images are processed and the numbers of positive
cells for each channel and each condition are determined.
In addition,
HT29 cells are treated with increasing concentrations of ARQ-197 for 32
hours in the absence or the presence of 25, 50, and 100 μM ZvAD-FMK
(irreversible general Caspase Inhibitor), and the same procedures are
undertaken. All experiments are done in triplicate. To determine whether
the apoptotic effect is due to c-Met inhibition, the effect of ARQ-197
when glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) and c-Met are
knocked down using siRNA is investigated.
HT29, MKN-45, and MDA-MB-231
cells are transfected with a nontargeted control siRNA, a gapgh-targeted
control siRNA, or a met-targeted siRNA. After 3 days, c-Met, GAPDH, and
β-actin expression levels are determined using specific antibodies. To
determine if the effect is caspase dependent, HT29, MKN-45, and
MDA-MB-231 cells are transfected with a met-targeted siRNA for 2 days
and incubated in the absence or the presence of increasing
concentrations of ZvAD-FMK for 1 additional day. A nontargeted siRNA and
a gapgh-targeted siRNA (siRNA GAPDH) are also transfected in parallel,
as controls. Cells are then stained with Annexin V-FITC and propidium
iodide, and the percentage of apoptotic cells is determined.
Contact us if you need more details on 905854-02-6. We are ready to answer your questions on packaging, logistics, certification or any other aspects about Tivantinib 905854-02-6、ARQ 197 905854-02-6. If these products fail to match your need, please contact us and we would like to provide relevant information.
Product Categories : Protein Tyrosine Kinase > c-Met Inhibitor
Other Products
Hot Products
Astragaloside AChlortetracycline HCl 64-72-2Paclitaxel 33069-62-4Dexamethasone Acetate 1177-87-3Dinaciclib (SCH727965) 779353-01-4CHIR-124 405168-58-3Ro3280 1062243-51-9TAME 901-47-3CCG-1423 285986-88-110058-F4 403811-55-2Dabigatran (BIBR 953) 211914-51-1H 89 2HCl 130964-39-5T0901317 293754-55-9Aprepitant 170729-80-3Turofexorate Isopropyl (XL335) 629664-81-9BMS-378806 357263-13-9