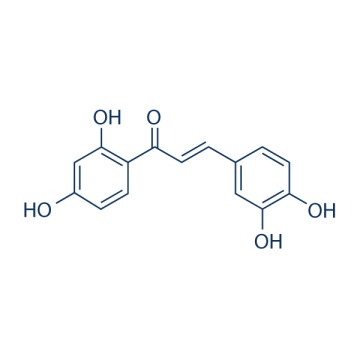
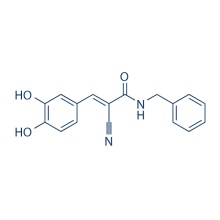
Butein 487-52-5
Product Description
.cp_wz table {border-top: 1px solid #ccc;border-left:1px solid #ccc; } .cp_wz table td{border-right: 1px solid #ccc; border-bottom: 1px solid #ccc; padding: 5px 0px 0px 5px;} .cp_wz table th {border-right: 1px solid #ccc;border-bottom: 1px solid #ccc; padding: 5px 0px 0px 5px;}
Molecular Weight:
272.25 Butein, a plant polyphenol isolated from Rhus verniciflua, is able to inhibit the activation of Protein Tyrosine Kinase, NF-κB and STAT3, also inhibits EGFR
Biological Activity
Butein inhibits the epidermal growth factor (EGF)-stimulated
auto-phosphotyrosine level of EGF receptor in HepG2 cells, and also
inhibits tyrosine-specific protein kinase activities of EGF receptor and
p60c-src with IC50 of 65 μM in vitro. The inhibition is
competitive to ATP and non-competitive to the phosphate acceptor, poly
(Glu, Ala, Tyr) 6:3:1 for EGF receptor tyrosine kinase. In contrast,
Butein non-significantly inhibits the activities of serine- and
threonine-specific protein kinases such as PKC or PKA.
Butein inhibits Nuclear Factor(NF)-κB and NF-κB-regulated gene
expression through direct inhibition of IκBα Kinase β on Cysteine 179
Residue. Butein (10 μM) inhibits over 90% iNOS and COX-2
expression, as well as nitrite and TNF-α production in LPS-stimulated
RAW 264.7 cells. Butein (10 μM) inhibits LPS-induced DNA binding
activity of NF-κB, which is mediated through inhibition of the
degradation of inhibitory factor-κB and phosphorylation of Erk1/2 MAP
kinase, as well as increases binding of the osteopontin a vb3 integrin
receptor.
Butein (20 μM) treatment induces morphologic
changes of bladder cancer cells BLS(M) from elongated morphology to
rounded epithelial-like cells, accompanied by downregulation of
vimentin, and gaining of E-cadherin compared to untreated control cells,
indicating the reversal of mesenchymal-like phenotype. Butein (20 μM)
suppresses motility and invasion capacity of BLS(M) cells, and reverts
EMT-like phenotype induced by TNF-α, through the ERK1/2 and NF-κB
signaling pathways.
Butein inhibits the constitutive
activation of STAT3 in HepG2 cells in a dose-dependent manner, with
maximum inhibition occurring at 50 μM, mediated through the inhibition
of activation of upstream kinases c-Src and Janus-activated kinase2.
Butein (50 μM) also could completely inhibit IL-6-induced STAT3
phosphorylation in SNU-387 cells. Butein downregulates the expression of
cyclin D1, Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, survivin, and VEGF, markers of STAT3
activation.
Butein (50 μM) significantly enhance the apoptotic effects
of doxorubicin from 18% to 55% and of paclitaxel from 15% to 42%. [5] Butein is as a powerful antioxidant against lipid and LDL peroxidation.
Butein inhibits iron-induced lipid peroxidation in rat brain homogenate
with an IC50 of 3.3 μM. Butein is as potent α-tocopherol in reducing
the stable free radical diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) with IC0.2 of
9.2 μM.
Butein also inhibits the activity of xanthine oxidase with an
IC50 of 5.9 μM. Butein scavenges the peroxyl radical derived from
2,2-azobis(2-amidinopropane) dihydrochloride (AAPH) in aqueous phase.
Furthermore, Butein inhibits copper-catalyzed oxidation of human
low-density lipoprotein (LDL) in a concentration-dependent manner.
Butein is a chelator of ferrous and copper ions.
Butein at 2 mg/kg induces significant inhibition of hepatocellular tumor
growth compared with the corn oil-treated controls. At necropsy on day
22 after initial treatment, there is more than 2-fold decrease in tumor
growth in the Butein-treated group (mean relativetumor burden, 3.90)
compared with the control group (8.46), associated with reduced
constitutive p-STAT3 (9% vs 81% of vehicle group), Bcl-2 levels (26% vs
96% of vehicle group), and increased caspase-3 level (98% vs 21% of
vehicle group) in HCC tumor tissues.
Butein shows
antifibrogenic activity. Butein (25 mg/kg/day) reduces serum AST and ALT
activation to 35% and 69%, respectively, of control CCl4-induced
rat levels. Butein (25 mg/kg/day) reduces liver hydroxyproline contents
and TBAR4 concentration to 54% and 54%, respectively. α1(I) collagen
and TIMP-1 expression in Butein-treated rats is 28% and 20.3% compared
with the values for the respective CCl4-treated control.
Contact us if you need more details on 487-52-5. We are ready to answer your questions on packaging, logistics, certification or any other aspects about Butein 487-52-5、487-52-5 Butein. If these products fail to match your need, please contact us and we would like to provide relevant information.
Molecular Weight:
272.25 Butein, a plant polyphenol isolated from Rhus verniciflua, is able to inhibit the activation of Protein Tyrosine Kinase, NF-κB and STAT3, also inhibits EGFR
Biological Activity
Butein inhibits the epidermal growth factor (EGF)-stimulated
auto-phosphotyrosine level of EGF receptor in HepG2 cells, and also
inhibits tyrosine-specific protein kinase activities of EGF receptor and
p60c-src with IC50 of 65 μM in vitro. The inhibition is
competitive to ATP and non-competitive to the phosphate acceptor, poly
(Glu, Ala, Tyr) 6:3:1 for EGF receptor tyrosine kinase. In contrast,
Butein non-significantly inhibits the activities of serine- and
threonine-specific protein kinases such as PKC or PKA.
Butein inhibits Nuclear Factor(NF)-κB and NF-κB-regulated gene
expression through direct inhibition of IκBα Kinase β on Cysteine 179
Residue. Butein (10 μM) inhibits over 90% iNOS and COX-2
expression, as well as nitrite and TNF-α production in LPS-stimulated
RAW 264.7 cells. Butein (10 μM) inhibits LPS-induced DNA binding
activity of NF-κB, which is mediated through inhibition of the
degradation of inhibitory factor-κB and phosphorylation of Erk1/2 MAP
kinase, as well as increases binding of the osteopontin a vb3 integrin
receptor.
Butein (20 μM) treatment induces morphologic
changes of bladder cancer cells BLS(M) from elongated morphology to
rounded epithelial-like cells, accompanied by downregulation of
vimentin, and gaining of E-cadherin compared to untreated control cells,
indicating the reversal of mesenchymal-like phenotype. Butein (20 μM)
suppresses motility and invasion capacity of BLS(M) cells, and reverts
EMT-like phenotype induced by TNF-α, through the ERK1/2 and NF-κB
signaling pathways.
Butein inhibits the constitutive
activation of STAT3 in HepG2 cells in a dose-dependent manner, with
maximum inhibition occurring at 50 μM, mediated through the inhibition
of activation of upstream kinases c-Src and Janus-activated kinase2.
Butein (50 μM) also could completely inhibit IL-6-induced STAT3
phosphorylation in SNU-387 cells. Butein downregulates the expression of
cyclin D1, Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, survivin, and VEGF, markers of STAT3
activation.
Butein (50 μM) significantly enhance the apoptotic effects
of doxorubicin from 18% to 55% and of paclitaxel from 15% to 42%. [5] Butein is as a powerful antioxidant against lipid and LDL peroxidation.
Butein inhibits iron-induced lipid peroxidation in rat brain homogenate
with an IC50 of 3.3 μM. Butein is as potent α-tocopherol in reducing
the stable free radical diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) with IC0.2 of
9.2 μM.
Butein also inhibits the activity of xanthine oxidase with an
IC50 of 5.9 μM. Butein scavenges the peroxyl radical derived from
2,2-azobis(2-amidinopropane) dihydrochloride (AAPH) in aqueous phase.
Furthermore, Butein inhibits copper-catalyzed oxidation of human
low-density lipoprotein (LDL) in a concentration-dependent manner.
Butein is a chelator of ferrous and copper ions.
Butein at 2 mg/kg induces significant inhibition of hepatocellular tumor
growth compared with the corn oil-treated controls. At necropsy on day
22 after initial treatment, there is more than 2-fold decrease in tumor
growth in the Butein-treated group (mean relativetumor burden, 3.90)
compared with the control group (8.46), associated with reduced
constitutive p-STAT3 (9% vs 81% of vehicle group), Bcl-2 levels (26% vs
96% of vehicle group), and increased caspase-3 level (98% vs 21% of
vehicle group) in HCC tumor tissues.
Butein shows
antifibrogenic activity. Butein (25 mg/kg/day) reduces serum AST and ALT
activation to 35% and 69%, respectively, of control CCl4-induced
rat levels. Butein (25 mg/kg/day) reduces liver hydroxyproline contents
and TBAR4 concentration to 54% and 54%, respectively. α1(I) collagen
and TIMP-1 expression in Butein-treated rats is 28% and 20.3% compared
with the values for the respective CCl4-treated control.
Contact us if you need more details on 487-52-5. We are ready to answer your questions on packaging, logistics, certification or any other aspects about Butein 487-52-5、487-52-5 Butein. If these products fail to match your need, please contact us and we would like to provide relevant information.
Product Categories : Protein Tyrosine Kinase > EGFR Inhibitor
Other Products
Hot Products
Astragaloside AChlortetracycline HCl 64-72-2Paclitaxel 33069-62-4Dexamethasone Acetate 1177-87-3Dinaciclib (SCH727965) 779353-01-4CHIR-124 405168-58-3Ro3280 1062243-51-9TAME 901-47-3CCG-1423 285986-88-110058-F4 403811-55-2Dabigatran (BIBR 953) 211914-51-1H 89 2HCl 130964-39-5T0901317 293754-55-9Aprepitant 170729-80-3Turofexorate Isopropyl (XL335) 629664-81-9BMS-378806 357263-13-9