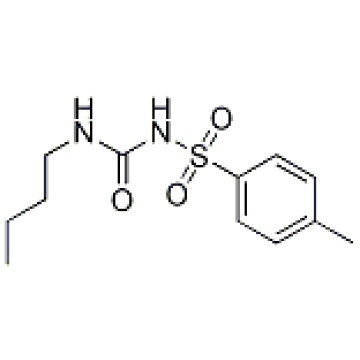
Tolbutamide 64-77-7
Product Description
.cp_wz table {border-top: 1px solid #ccc;border-left:1px solid #ccc; } .cp_wz table td{border-right: 1px solid #ccc; border-bottom: 1px solid #ccc; padding: 5px 0px 0px 5px;} .cp_wz table th {border-right: 1px solid #ccc;border-bottom: 1px solid #ccc; padding: 5px 0px 0px 5px;}
Molecular Weight:
270.35 Tolbutamide is an inhibitor of potassium channel, used for type II diabetes.
Biological Activity
Tolbutamide belongs to a class of medications called sulfonylureas.
Tolbutamide lowers blood sugar by causing the pancreas to produce
insulin (a natural substance that is needed to break down sugar in the
body) and helping the body use insulin efficiently. This medication will
only help lower blood sugar in people whose bodies produce insulin
naturally.
Tolbutamide is not used to treat type 1 diabetes (condition
in which the body does not produce insulin and, therefore, cannot
control the amount of sugar in the blood) or diabetic ketoacidosis (a
serious condition that may occur if high blood sugar is not treated).
Tolbutamide inhibits both the basal and the cyclic AMP-stimulated
protein kinase activities and the IC50 of Tolbutamide is 4 mM.
Similar
Tolbutamide concentrations are required for half maximal inhibition of
in vitro lipolysis induced by hormones (norepinephrine and ACTH) or by
dibutyryl cyclic AMP plus theophylline. Tolbutamide also inhibits both
soluble and membrane-bound protein kinase from canine heart. The
Tolbutamide inhibition of adipose tissue cyclic AMP-dependent protein
kinase is one possible explanation for the antilipolytic effects of this
drug.
Tolbutamide inhibits C6-glioma cell proliferation
by increasing Cx43, which correlates with a reduction in pRb
phosphorylation due to the up-regulation of the Cdk Inhibitors p21 and
p27. Cytosolic nucelotides enhance the Tolbutamide
sensitivity of the ATP-dependent K+ channel in mouse pancreatic B cells
by their combined actions at inhibitory and stimulatory receptors.
Tolbutamide inhibits glucagon-induced phosphorylation of the
bifunctional enzyme protein in a dose-dependent manner. By adding 2 mM
Tolbutamide, reduces activity of 6PF-2-K and increased activity of
Fru-2,6-P2ase in the presence of 10(-9) M glucagon are partially
restored. The present results suggest the possibility that Tolbutamide
modulates the activity of hepatic 6PF-2-K/Fru-2,6-P2ase through
inhibiting a phosphorylation of the enzyme protein.
450 mg Tolbutamide/kg/day given for 7 days significantly increases the
binding of insulin to isolated adipocytes. The binding curves reflect an
increase in the number of receptor sites rather than in the affinity.
The effect is associated with an enhanced response to insulin of the
adipose tissue, since the fat cells obtained from animals treated with
Tolbutamide convert significantly more glucose to lipids in the presence
of insulin than those obtained from the control group. However, the
augmentation of insulin binding sites is observed only at a large
tolbutamide dosage, which reduces the pancreatic insulin content, the
secretory response of the isolated pancreas, and the serum insulin
levels. Smaller doses, sufficient to produce metabolic effects via a
stimulation of insulin secretion, do not provide additional insulin
binding sites.
Contact us if you need more details on 64-77-7. We are ready to answer your questions on packaging, logistics, certification or any other aspects about Tolbutamide 64-77-7、64-77-7 Tolbutamide. If these products fail to match your need, please contact us and we would like to provide relevant information.
Molecular Weight:
270.35 Tolbutamide is an inhibitor of potassium channel, used for type II diabetes.
Biological Activity
Tolbutamide belongs to a class of medications called sulfonylureas.
Tolbutamide lowers blood sugar by causing the pancreas to produce
insulin (a natural substance that is needed to break down sugar in the
body) and helping the body use insulin efficiently. This medication will
only help lower blood sugar in people whose bodies produce insulin
naturally.
Tolbutamide is not used to treat type 1 diabetes (condition
in which the body does not produce insulin and, therefore, cannot
control the amount of sugar in the blood) or diabetic ketoacidosis (a
serious condition that may occur if high blood sugar is not treated).
Tolbutamide inhibits both the basal and the cyclic AMP-stimulated
protein kinase activities and the IC50 of Tolbutamide is 4 mM.
Similar
Tolbutamide concentrations are required for half maximal inhibition of
in vitro lipolysis induced by hormones (norepinephrine and ACTH) or by
dibutyryl cyclic AMP plus theophylline. Tolbutamide also inhibits both
soluble and membrane-bound protein kinase from canine heart. The
Tolbutamide inhibition of adipose tissue cyclic AMP-dependent protein
kinase is one possible explanation for the antilipolytic effects of this
drug.
Tolbutamide inhibits C6-glioma cell proliferation
by increasing Cx43, which correlates with a reduction in pRb
phosphorylation due to the up-regulation of the Cdk Inhibitors p21 and
p27. Cytosolic nucelotides enhance the Tolbutamide
sensitivity of the ATP-dependent K+ channel in mouse pancreatic B cells
by their combined actions at inhibitory and stimulatory receptors.
Tolbutamide inhibits glucagon-induced phosphorylation of the
bifunctional enzyme protein in a dose-dependent manner. By adding 2 mM
Tolbutamide, reduces activity of 6PF-2-K and increased activity of
Fru-2,6-P2ase in the presence of 10(-9) M glucagon are partially
restored. The present results suggest the possibility that Tolbutamide
modulates the activity of hepatic 6PF-2-K/Fru-2,6-P2ase through
inhibiting a phosphorylation of the enzyme protein.
450 mg Tolbutamide/kg/day given for 7 days significantly increases the
binding of insulin to isolated adipocytes. The binding curves reflect an
increase in the number of receptor sites rather than in the affinity.
The effect is associated with an enhanced response to insulin of the
adipose tissue, since the fat cells obtained from animals treated with
Tolbutamide convert significantly more glucose to lipids in the presence
of insulin than those obtained from the control group. However, the
augmentation of insulin binding sites is observed only at a large
tolbutamide dosage, which reduces the pancreatic insulin content, the
secretory response of the isolated pancreas, and the serum insulin
levels. Smaller doses, sufficient to produce metabolic effects via a
stimulation of insulin secretion, do not provide additional insulin
binding sites.
Contact us if you need more details on 64-77-7. We are ready to answer your questions on packaging, logistics, certification or any other aspects about Tolbutamide 64-77-7、64-77-7 Tolbutamide. If these products fail to match your need, please contact us and we would like to provide relevant information.
Product Categories : Transmembrane Transporters > Potassium Channel Inhibitor
Other Products
Hot Products
Astragaloside AChlortetracycline HCl 64-72-2Paclitaxel 33069-62-4Dexamethasone Acetate 1177-87-3Dinaciclib (SCH727965) 779353-01-4CHIR-124 405168-58-3Ro3280 1062243-51-9TAME 901-47-3CCG-1423 285986-88-110058-F4 403811-55-2Dabigatran (BIBR 953) 211914-51-1H 89 2HCl 130964-39-5T0901317 293754-55-9Aprepitant 170729-80-3Turofexorate Isopropyl (XL335) 629664-81-9BMS-378806 357263-13-9